Microsoft Windows is a family of proprietary graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. The first member of the Windows family, Windows 1.0, was released on November 20, 1985. Active Windows families include Windows NT and Windows IoT; these may encompass subfamilies, (e.g. Windows Server or Windows Embedded Compact) (Windows CE). Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, which was aimed at home users, and Windows Mobile and Windows Phone, which were aimed at mobile devices.
Out latest articles about Microsoft Windows
More about Microsoft Windows
Windows NT was the first fully 32-bit version of Windows and was designed for business users. It was released on July 27, 1993. Windows NT included several new features, such as the ability to run multiple programs simultaneously and support for networked computers.
Windows IoT is a version of Windows designed for devices that are connected to the Internet of Things (IoT). It was released on August 2016. Windows IoT includes support for sensors, actuators, and other devices that are commonly used in IoT applications.
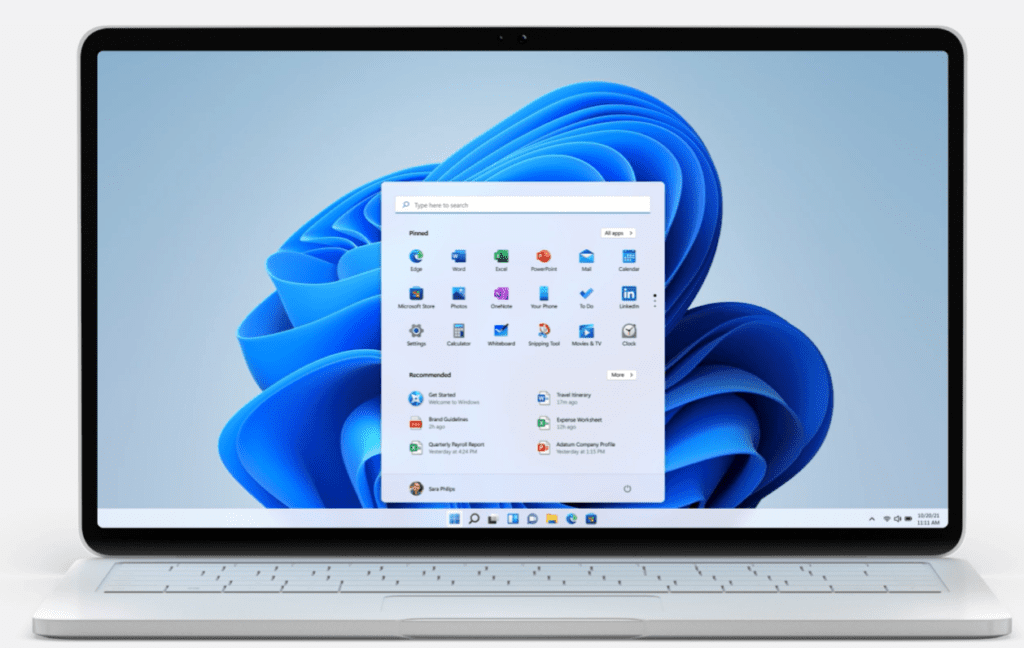
The most recent release of Microsoft Windows is Windows 11, which was released on October 20, 2020. This latest version includes a number of new features and improvements, such as an updated Start menu, a new taskbar, and support for multiple monitors. Windows 11 also includes a new version of the Microsoft Edge web browser.
Microsoft Windows is a widely used operating system with a long history. It has evolved over the years to include many different features and cater to various sectors of the computing industry. Whether you’re looking for an operating system for your home or business, there’s a good chance that Microsoft Windows has what you need.
Features of Microsoft Windows
Over the years, Microsoft Windows has undergone a major transformation. The latest version, Windows 11, is a far cry from the first version of Windows that was released back in 1985. However, some of the core features of Windows remain the same. Here are just a few of the features that have made Windows one of the most popular operating systems in the world:
Ease of use: One of the things that has always set Windows apart from other operating systems is its ease of use. The user interface is designed to be simple and intuitive, and even users with little computer experience can quickly learn how to use it. In addition, Windows comes with a variety of built-in applications that make it easy to perform common tasks, such as sending email or browsing the web.
Flexibility: Another key advantage of Windows is its flexibility. Unlike some operating systems that are designed for specific types of computer hardware, Windows can be installed on a wide range of devices, from desktop PCs to laptops to tablets. In addition, users can customize their Windows experience to suit their individual needs, whether they want a simple interface or more advanced features.
Compatibility: One of the biggest concerns for users when switching to a new operating system is whether their existing software and hardware will be compatible. With Windows, there is no need to worry about compatibility issues. The majority of software applications and hardware devices are compatible with Windows, making it easy to switch from another operating system without losing any functionality.
These are just a few of the reasons why Microsoft Windows is still one of the most popular operating systems in use today. Whether you’re looking for an easy-to-use interface or flexibility and compatibility, Windows has something to offer everyone.
How to use Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a graphical user interface (GUI) operating system that was first released in 1985. Since then, it has become the most widely used operating system in the world. Using Windows is relatively simple and user-friendly.
The Start menu, located in the bottom left corner of the screen, is the main way to navigate and find programs or files on your computer. The Start menu can be customized to display your most frequently used programs, making it easy to find what you need.
The taskbar, located at the bottom of the screen, displays open programs and files as well as notifications from your computer. Right-clicking on the taskbar gives you options to customize its appearance or behavior. For example, you can choose to have the taskbar always visible or only visible when you hover your mouse over it.
Windows also includes a search function that makes it easy to find files or programs on your computer. Simply type in what you’re looking for and Windows will display a list of matching results.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, Microsoft Windows is a great operating system for both productivity and entertainment.
Some Tips and tricks for using Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is the most popular operating system in the world, and for good reason. It is user-friendly, reliable and packed with features. However, there are still many users who are not taking full advantage of all that Windows has to offer. Here are a few tips and tricks to help you get the most out of your Windows experience:
- Get to know the Start menu. The Start menu is your gateway to all of the programs and features on your computer. Take some time to explore all of the options available to you.
- Make use of keyboard shortcuts. Keyboard shortcuts can save you a lot of time and make using Windows more efficient. For example, the Windows key + E opens File Explorer, and Windows key + L locks your computer.
- Use Cortana for hands-free assistance. Cortana is Microsoft’s digital assistant, and she can be a big help when you’re using Windows. She can answer questions, set reminders and even open programs for you. Just click the Cortana icon in the taskbar and say what you need.
- Keep your computer up-to-date. Microsoft regularly releases updates for Windows, which include new features as well as security improvements. Be sure to install any updates as soon as they are available to keep your computer running smoothly.
By following these tips, you can make sure that you are getting the most out of your Windows experience.
Brief History of Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a graphical operating system (GUI) developed and released by Microsoft Corporation. It was first released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical extension for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in GUIs.
Windows 1.0 was not very successful, but the release of Windows 2.0 in 1987 increased its popularity. Windows 3.0, released in 1990, was a major upgrade and the first version to gain widespread adoption. By this time, Windows had become the dominant GUI on personal computers.
With the release of Windows 95, Microsoft further increased its lead over competitors such as Apple Computer and IBM. Today, Microsoft Windows is the most widely used GUI in the world and has been installed on over one billion computers.
Despite its ubiquity, Microsoft has continued to innovate with new versions of Windows, such as Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, and 10. Each new version introduces new features and improvements that keep users coming back for more.
Windows 1.0
In November 1985, Microsoft released the first version of Windows, a graphical user interface (GUI) that allowed users to interact with their computers using a mouse and a keyboard instead of text commands.
The initial release of Windows 1.0 was met with mixed reviews; some praised the new GUI for its ease of use, while others criticized it for its lack of features and speed. Despite these early challenges, Windows quickly became the most popular operating system in the world.
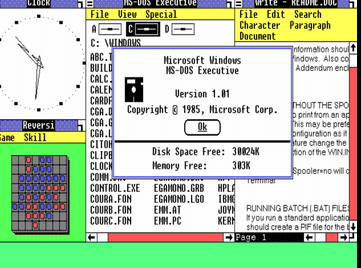
In part, this success was due to the release of subsequent versions of Windows that addressed the criticisms leveled at the original release. However, it was also due to the fact that, at a time when computer use was becoming more widespread, Windows made it possible for average users to harness the power of personal computers. As a result, Windows remains one of the most influential pieces of software ever created.
Windows 2.0
Windows 2.0 was a significant update to the Windows operating system, released in 1987. It added support for multitasking, expanded the capabilities of the graphical user interface, and allowed programs to access more than 640 kB of memory.
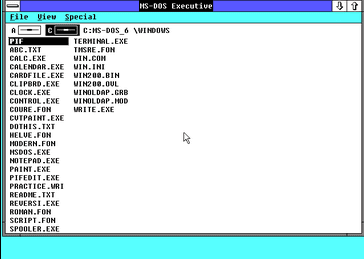
These improvements made Windows 2.0 much more capable than its predecessor, and it quickly became the most popular PC operating system. However, Windows 2.0 was not without its problems. It was still based on the MS-DOS operating system, which limited its overall performance.
In addition, many users found the new interface confusing and difficult to use. As a result, Microsoft released several subsequent versions of Windows 2.0 before finally moving on to a new operating system.
Windows 3.1
Developed by Microsoft, Windows 3.1 was released on April 6, 1992 and was the first successfully popular version of Windows. It became well known for its enhanced graphical user interface and improved performance over its predecessor, Windows 3.0.
Building on the success of Windows 3.0, 3.1 featured several new features including updates to the Program Manager, File Manager and Print Spooler; support for TrueType fonts; better networking capabilities; and support for audio CDs.

Windows 3.1 also included a new game, Solitaire, which quickly became a fan favorite. Although it was eventually replaced by newer versions of Windows, Windows 3.1 remains an important part of Microsoft’s history and helped to establish the company as a major player in the software industry.
Windows 95
Windows 95 was a major release of Microsoft Windows, released on August 24, 1995. It was a release that featured significantly improved performance, a more user-friendly interface, and greater integration with the internet.
Prior to its release, Windows 3.1 had been the most popular version of Windows, but Windows 95 quickly surpassed it in terms of both users and market share.
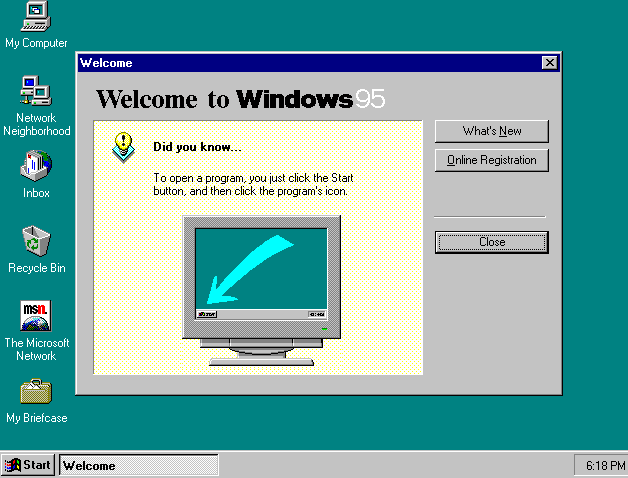
In addition to its improved performance and usability, Windows 95 also introduced a number of features that would become standard in future versions of Windows, including the Start button and the taskbar.
While it is no longer supported by Microsoft, many people continue to use Windows 95 today, either because they are unable to upgrade or because they prefer its simpler interface. Regardless of its age, Windows 95 remains an important release in the history of Microsoft Windows.
Windows 98
The windows 98 operating system was released in 1998 by Microsoft. It was the successor to the highly successful Windows 95, and it introduced a number of new features that made it even easier to use.
One of the most notable new features was the inclusion of the Web Explorer web browser, which made surfing the internet much simpler.
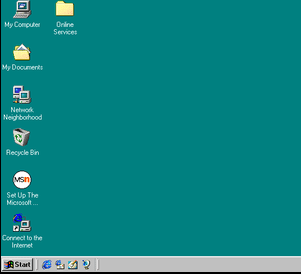
Another major change was the introduction of the Active Desktop, which allowed users to customize their desktop with links to their favorite websites. Windows 98 also featured improvements to performance and stability, making it one of the most popular versions of Windows ever released.
Despite being released over 20 years ago, many people still continue to use Windows 98 today due to its simplicity and reliability.
Windows ME (Millennium Edition)
Windows ME (codename Millennium Edition) is a graphical operating system developed by Microsoft as part of the Windows 9x series. It was released to manufacturing on June 19, 2000, and released to retail on September 14, 2000.
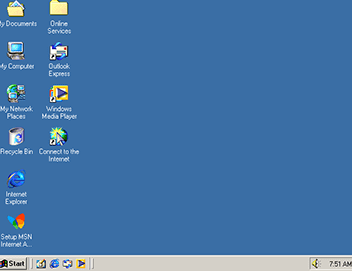
Unlike other versions of Windows, ME was targeted primarily at home users. It included several new features such as System Restore, Internet Explorer 5.5, Windows Movie Maker, and Microsoft Messenger. However, it was also criticized for being buggy and unstable.
As a result, it was replaced by Windows XP just over a year after its release. Despite its short lifespan, Windows ME is still remembered by many as one of the worst operating systems ever made.
Windows XP
Windows XP was a personal computer operating system that was produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and generally retail on October 25, 2001.
Windows XP was a major release of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, being the successor to both Windows 2000 Professional and Windows Me.
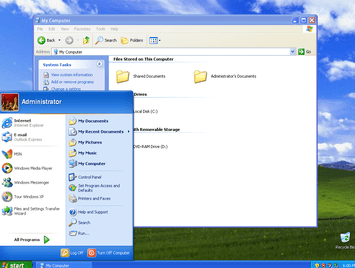
It introduced a significantly redesigned graphical user interface and was the first version of Windows to use product activation in an effort to reduce its copyright infringement. It was succeeded by Windows Vista.
Although still used on some personal computers today, it is no longer supported by Microsoft, as they have ended all support for the operating system as of April 8, 2014.
Despite this, many users continue to use it due to its simplicity and stability when compared to more recent versions of Windows. Some users have even taken measures to keep it running on newer hardware by using unofficial service packs and modifications such as “Old New Explorer”.
However, without support from Microsoft and security risks posed by continuing to use an unsupported operating system, it is generally advised that users migrate to a supported version of Windows.
For those who cannot or do not want to do this, various Linux distributions such as Ubuntu MATE are available which can provide support for years after their official end-of-life date. With proper care, a computer running Windows XP can continue to be used for many years after its official end-of-life.
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a line of operating systems produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs.
First introduced in January 2007, Vista was designed to address the concerns of users about the Windows XP operating system, which had been criticized for its security flaws and vulnerabilities.
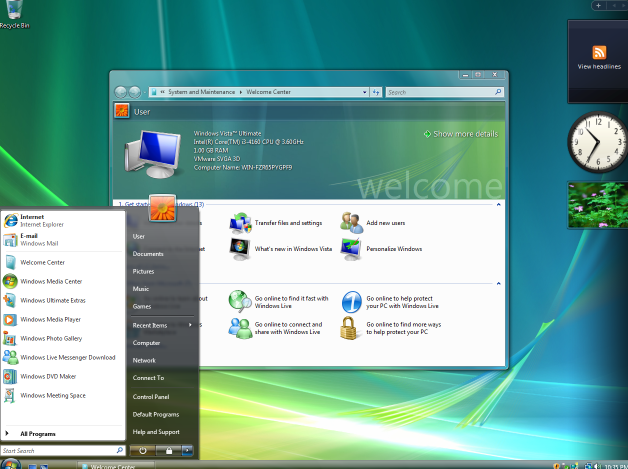
Vista includes a number of features designed to improve security, including strengthened defenses against malware and spyware, as well as a new user account control system that prompts users for permission before allowing any changes to be made to the system.
In addition, Vista includes a number of other enhancements, such as improved support for connecting to wireless networks and new features for managing digital photos and music.
While Vista has been generally well-received by users and critics alike, there have been some criticisms leveled at the operating system, including its high hardware requirements and its tendency to be slower than XP on older computers.
Overall, however, Vista remains a popular choice for users looking for a reliable and feature-rich operating system.
Windows 7
Windows 7 is a personal computer operating system that was produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems.
It was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, 2009, less than three years after the release of its predecessor, Windows Vista. Windows 7’s server counterpart, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released at the same time.
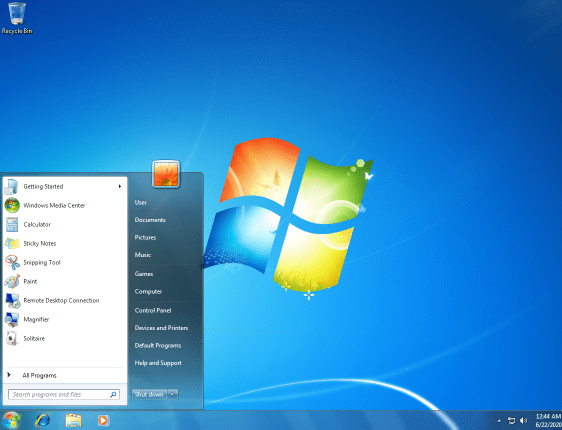
Windows 7 includes a number of new features, such as advances in touch and handwriting recognition, support for virtual hard disks, improved performance on multi-core processors, improved boot performance, and DirectAccess.
Windows 7 also includes a number of security and safety features to protect your computer from malware and other threats. With all these new features and more, Windows 7 is an excellent choice for your next operating system.
Windows 8 and 8.1
Although Windows 8 was initially met with some skepticism, it has since become a popular operating system, particularly among business users.
Windows 8.1 builds on the success of Windows 8, offering a number of improvements and new features.
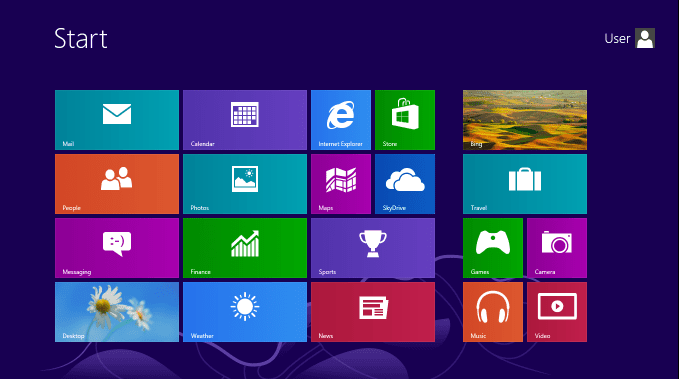
One of the most significant changes is the return of the Start button, which provides easy access to programs and files. In addition, Windows 8.1 includes upgraded versions of familiar apps like Internet Explorer and Skype, as well as new apps such as Bing Food & Drink and Bing Health & Fitness.
With its sleek design and powerful features, Windows 8.1 is a top choice for business users looking for a reliable and user-friendly operating system.
Windows 10
Despite its many features, Windows 10 has faced criticism for privacy concerns and a variety of bugs.
One of the most common complaints is that Windows 10 automatically collects data about users, including their location, search history, and the contents of their emails.

Microsoft has defended this practice by saying that the data is used to improve the user experience, but many people remain concerned about how their personal information is being used.
In addition, Windows 10 has been plagued by a number of software glitches, including problems with the Start menu, Cortana, and the Edge browser. While Microsoft has released updates to fix these issues, they have continued to cause frustration for many users.
Despite its challenges, Windows 10 remains the most popular operating system in the world.
Windows 11 (the current version as of this writing)
With the release of Windows 11, Microsoft has once again raised the bar for operating systems.
Building on the strong foundation of Windows 10, Windows 11 introduces a number of significant improvements, including a new Start menu, an updated taskbar, and a revised File Explorer.

In addition, Microsoft has made a number of changes under the hood, such as revamping the networking stack and improving security features. As a result, Windows 11 is faster, more reliable, and more secure than ever before.
Whether you’re a longtime Windows user or you’re making the switch from another operating system, Windows 11 is sure to impress.
Summary
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Windows families include Windows NT and Windows IoT; these may encompass subfamilies, (e.g. Windows Server or Windows Embedded Compact) (Windows CE).
Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows 11 (the current version as of this writing) builds on the strong foundation of Windows with a number of significant improvements, including a new Start menu, an updated taskbar, and a revised File Explorer. Whether you’re a longtime Windows user or you’re making the switch from another operating system, Windows 11 is sure to impress.
